Describe the Process of Crossing Over
Crossing over occurs in the first division of meiosis. It takes place in pachytene stage of prophase-I of meiosis.
Explain how the random alignment of homologous chromosomes.
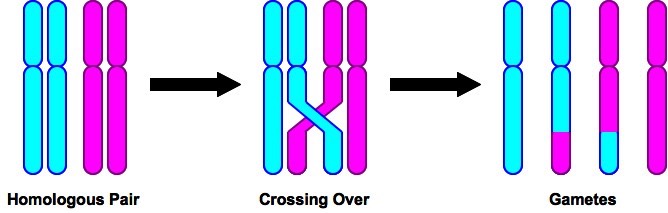
. Crossing over occurs between these. The process of crossing over occurs during meiosis. These chromosomes stay close together and Nonsister chromatids exchange genetic material an event also known as Crossing over.
Crossing over refers to the interchange of parts between non-sister chromatids of homologus chromosomes during meiotic prophase pachytene. During crossing over part of one chromosome is exchanged with another. Alleles in.
It occurs most often during the first meiotic division. The 2 sister chromatids intersect and exchange some of their genetic material. This process occurs during the prophase of meiosis I.
Chromosomes get twisted around each other forming a chiasma so some of the alleles are exchanged. Hence it is of great importance in the evolution. Crossing over can be observed visually after the exchange as chiasmata.
Describe the process that results i the formation of a tetrad. What effect does crossing-over process have on linked genes with respect to the relative distance on the chromosome. Crossing over occurs when a paternal chromatid exchanges part of itself with the maternal chromatid so some alleles that were on one chromatid are now on the other.
Crossing over is simply the exchange of genetic material between two homologous chromosomes to give rise to recombinant chromosomes. Describe the process of crossing over detailing at what stage of the cell cycle it occurs. This crossing over - crossing over is the swapping of genetic material that occurs in the germ line.
Phenomenon that occurs in Prophase I of meiosis between 2 sister chromatids on different chromosomes of an Homologous pair. This increases genetic diversity because there are new combinations of alleles every time crossing over occurs. Then exchange of a small segment of chromatid genetic material between non sister chromatids takes place.
In other words crossing over results from exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids involving breakage and reunion at. Crossing over is a widespread phenomenon which is known to occur in all the higher organisms as well as in most bacteria and viruses. Crossing over is a cellular process that happens during meiosis when chromosomes of the same type are lined up.
See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 3. Added an answer on June 15 2020 at 1243 pm Non sister chromatids overlap or coil each other. Occurs during prophase Iduring meiosis.
Crossing-over is a unique phenomenon which occurs only in the prophase I stage of meiotic division ie. This problem has been solved. The synaptonemal complex supports the exchange of chromosomal segments between non-sister homologous chromatids a process called crossing over.
At that stage each chromosome has replicated into two strands called sister chromatids. When did the chromosomes cross. During the formation of egg and sperm cells also known as meiosis paired chromosomes froms each parent align so that similar DNA Sequences from the paired chromosomes cross over one another.
When two chromosomes one from the mother and one from the father line up parts of the chromosome can be switched. Genetic recombination happens as a result of the separation of genes that occurs during gamete formation in meiosis the random uniting of these genes at fertilization and the transfer of genes that takes place between chromosome pairs in a process known as crossing over. Crossing over is the process of swapping DNA sequences between the chromatids of paired homologous chromosomes.
Homologous separates and move to the opposite ends of the cell wh. In prophase I homologous chromosomes align lengthwise or pair with each other and exchange of genetic material between the two chromosomes takes place which is known as crossing over. Crossing over allows alleles on DNA.
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces four haploid gametes from a. The process which results in recombination by exchange of the segments between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes is called as crossing over. The result is a hybrid chromosome with a unique pattern of genetic material.
View the full answer. Describe the process of crossing over. Up to 10 cash back Crossing over is a process that happens between homologous chromosomes in order to increase genetic diversity.
Crossing-over Crossing-over is the process by which homologous chromosomes exchange segments with each other. Recombination Versus Crossing Over. In prophase I homologous chromosomes undergo a process called synapsis whereby they pair up to form a bivalent or tetrad The homologous chromosomes are held together at points called chiasmata singular.
The process of exchange of genetic material between non sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes is known as crossing over. It is the process whereby nonsister chromatids of homologous chromosomes similar but non-identical chromosomes from male and female parents exchange their genetic material. Describe the process of crossing over and how it increases genetic diversity.
The two chromosomes contain the same genes but may have different forms of the genes. Explain the reason for linked genes not following the pattern of inheritance discovered by Mendel. The two homologous chromosomes of a pair synapse or come together.
Upgrade to remove ads. This event is random happens by chance and can occur more than once in a bivalent. Crossing over crossing over process in genetics by which the two chromosomes of a homologous pair exchange equal segments with each other.
The exchange of genes between non sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes in this process leads to the production of recombinants. The early stages of meiosis involve pairing of homologous chromosomes and crossing over. When prometaphase begins each chromosome has been duplicated to form.
How can we calculate the distance of two linked genes. Crossing over creates genetic variation by exchanging DNA between two nonsister chromatids to produce genetically unique chromosomes.
Crossing Over With Its Importance Qs Study
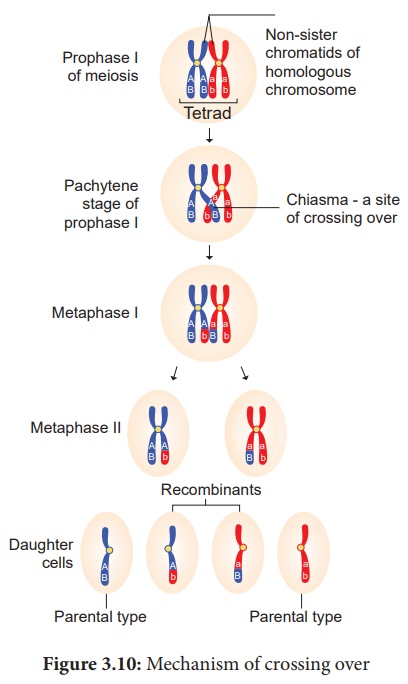
Crossing Over Mechanism Types Importance Recombination Botany Chromosomal Basis Of Inheritance

What Is Crossing Over Mention The Process Of Crossing Over Youtube

Comments
Post a Comment